metabolism 물질대사 (생화학)
metabolism
catolism: break down of organic matter ( cellular respiration)
anabolism: energy use to construct cell components ( protein, nucleic acids)
key biochemicals
amino acids, proteins
lipids
carbohydrates
nucleotides
coenzymes
minerals cofactors
catabolism
digestion
energy from organic compounds
energy transformation
oxidative phosphorylation
energy from inorganic compounds
energy from light

"simplified outline of catabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats'


The Bridging Step
Pyruvate + CoA + NAD+ --> acetyl CoA + CO2 + NADH
requires O2 as ultimate electron acceptor
Oxidative decarboxylation catalyzed by pyruvate dehydrogenase

pyruvate

CoA (coenzyme A)

acetyl CoA
Citric Acid Cycle
(tricarboxylic acid cycle, krebs cycle, szent-Györgyi-krebs cycle)
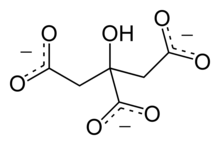
citrate anion
citrate
conjugate base of citric acid
intermediate in citric acid cycle (TCA)

products of citric acid cycle
from 1 round of the citric acid cycle
3 NADH
1FADH2
1GTP
2CO2
from Bridging step
1NADH
1CO2
regulation of bridging step
pyruvate dehydrogenase
-inhibited by (own product) : ATP, Acetyl CoA, NADH
-activated by (substrates) : AMP, Coa, Ca2+ (muscle), NAD+
regulation of citric acid cycle
citrate synthase
inhibited by: citrate, HADH, succinyl CoA, ATP
activated by: ADP
isocitrate dehydrogenase
inhibited by: ATP
activated by Ca2+, ADP
α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
inhibited by: succinyl CoA, NADH
activated by: Ca2+
citrate is prochiral
molecules can be converted achiral -> chiral in a single step
2 identical substituents attached to a sp3 hybridized atom
pro-R , pro-S
자료
http://courses.washington.edu/bioc440/lectures/overview.pdf
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metabolism
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Citric_acid_cycle
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prochiral
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Citrate
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acetyl-CoA
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pyruvate
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coenzyme_A